Dispersing agents or, in another term “Dispersants” are vital components of every formulator’s toolbox. They enable the maintenance of pigments and fillers till the point of painting and through the curing process, which guarantees intense, bright colors as well as unchanging gloss, waterproofing, and perpetual reliability across different batches. In addition to aesthetics, numerous important coating features depend upon your paint’s dispersant.
1. What are Dispersing Agents or Dispersants?
A dispersing agent (or simply dispersant) is an ingredient added in paints or other formulations that is meant to put a stop to flocculation of pigment and filler materials. Dispersants actively encourage and stabilize the suspension of tiny solid particles, including mineral fillers, pigments, and even additives, in a liquid medium. This allows for better efficiency during milling, boosting the strength of the tint, hiding power, and gloss, as well as increasing the water resistance in addition to ensuring consistency across different batches of paints, coatings, inks, construction slurries, and other materials.
All agents in dispersing have two basic components:
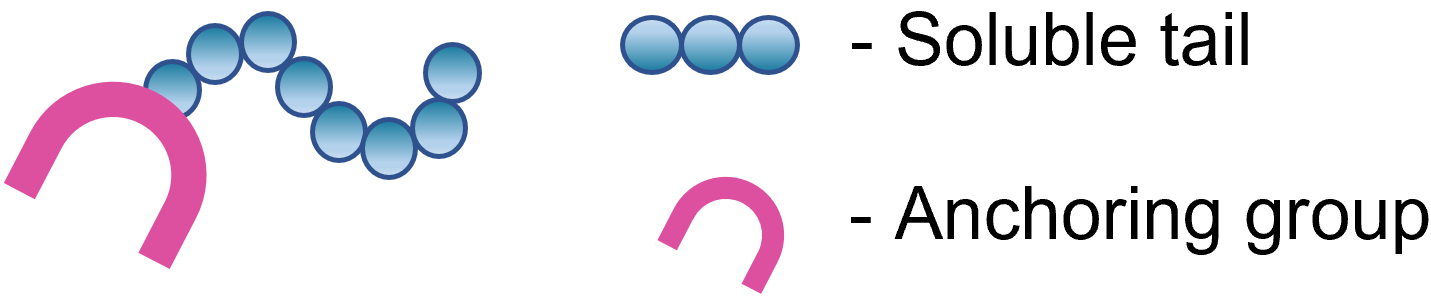
Anchoring Groups
These moieties display a posotive charge which is more than likely used for the surfaces of the particle, forming either physically or chemically bonded anchor sites.
Soluble Tails
Polymers or ionic chains found in the extensible tail are known as Soluble Tails, inserted in a matrix phase build barrier around single particles which aids.
Choosing the right dispersant has a direct impact on final product quality. A well-matched dispersant reduces milling time and viscosity, amplifies color strength, and delivers the lasting performance your customers demand.
2. How does a Dispersing Agent Work?
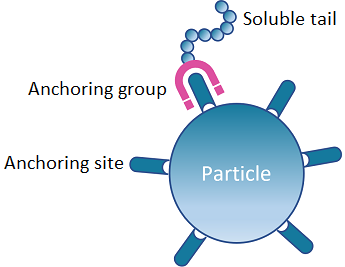
Dispersants operate by disrupting the natural attraction between solid particles, thereby preventing agglomeration or sedimentation:
Adsorption via Anchoring Groups
The anchor groups adsorb onto pigment or filler surfaces, latching onto chemical functional groups present on the particle.
Formation of a Protective Layer
Soluble tails extend outward, enveloping each particle in a “brush” layer.
Together, these domains generate two forms of repulsive force:
Electrostatic Repulsion
Charged dispersant tails impart like charges to particle surfaces, causing mutual repulsion.
Steric Repulsion
The physical thickness of the tail layer keeps particles from coming into close contact, safeguarding colloidal stability.
By continuously counteracting natural intermolecular attractions, dispersants maintain a finely divided suspension—ensuring smooth flow, uniform color, and stable rheology.
3. Key Features for Dispersing Agents
When choosing or formulating dispersants, focus on these feature benchmarks:
Captive Pigment Technology
Fast and efficient capture of all types of particle and chemical bonds.
Thickening Efficiency
Increase of viscosity at ideal conditions while maintaining processability at required levels.
Color & Hiding Power
Precision for best result of pigment dispersion leading to painting of deeper and more standard shades.
Finesse to Synthesis Altered Surface Enhancements
Improved control on amount of particulate matter improves width of smooth and bright film.
Mechanical and Water Resistance
Ability to withstand and function in humid or chemically harsh environments.
Steric/Achetype Polystyrene Support Conservation
Strong support to long term settlement under heat or mechanical stress.
Alkaline Versatile Temperature Range
Operational limits of low and high climates to better with acidic and alkaline systems.
Environment Friendly
Bans on volatile emissions - VOCs, easy to break down structures, and transnational policies.
4. Understanding Our (Beihua’s) Dispersants
Beihua’s HA-100 and HA-40 are engineered to deliver top-tier dispersion performance across multiple industries:
HA-100
Basic Information
Type: Polymeric polycarboxylate ether (PCE)
Appearance: Light-yellow liquid (40% solids)
Charge: Anionic
Main Uses
- High-performance cement and concrete dispersant
- Low-viscosity pigment dispersion in architectural and industrial coatings
- Rheology modifier in water-based inks and ceramics
Typical Applications
- Self-leveling Flooring: Optimizes pumpability and finish smoothness.
- Ready-Mix Concrete: Cuts water demand by up to 25%, boosting strength and workability.
- High-Color Pigment Concentrates: Achieves ultra-fine dispersions for deep, uniform shades.
HA-40
Basic Information
Type: Modified polyacrylate
Appearance: Clear to pale-yellow liquid (30% solids)
Charge: Non-ionic
Main Uses
- Dispersant for mineral fillers (e.g., CaCO₃, talc, silica)
- Flow and leveling aid in high-solids resin systems
- Stabilizer in latex and emulsion polymer formulations
Typical Applications
- PVC Compounding: Increases filler load without sacrificing processability or surface quality.
- UV-Curable Coatings: Ensures uniform nanoparticle distribution for scratch-resistant finishes.
- Waterborne Adhesives: Enhances tack, open time, and bond strength on porous substrates.
Conclusion
Formulators using Beihua's HA-100 and HA-40 Dispersing Agents will experience faster production, better end-product efficacy, and greater stability over time, all because of the soluble arms and anchoring groups. Enable concrete and coatings, inks and adhesives, and so many more products to reap the benefits of smooth rheology, color consistency, and strong suspension stability by interacting with cutting edge suspending agents. Improving a formulation by choosing a dispersant is diving straight into the center of innovation while propelling an enterprise forward. Non-formulating steps toward carrying a company as turning optimal dispersant selection shapes the very foundation of sustainable innovation, industry dominating efficiency, and unparalleled steadfast quality.
 cwc@jxbh-masterbatch.com
cwc@jxbh-masterbatch.com 嘉興北華高分子助剤有限公司 / 上海クリスタルウェルズ化学新材料有限公司 / 上海クリスタルウェルズ化学新材料有限公司
嘉興北華高分子助剤有限公司 / 上海クリスタルウェルズ化学新材料有限公司 / 上海クリスタルウェルズ化学新材料有限公司


































